Description
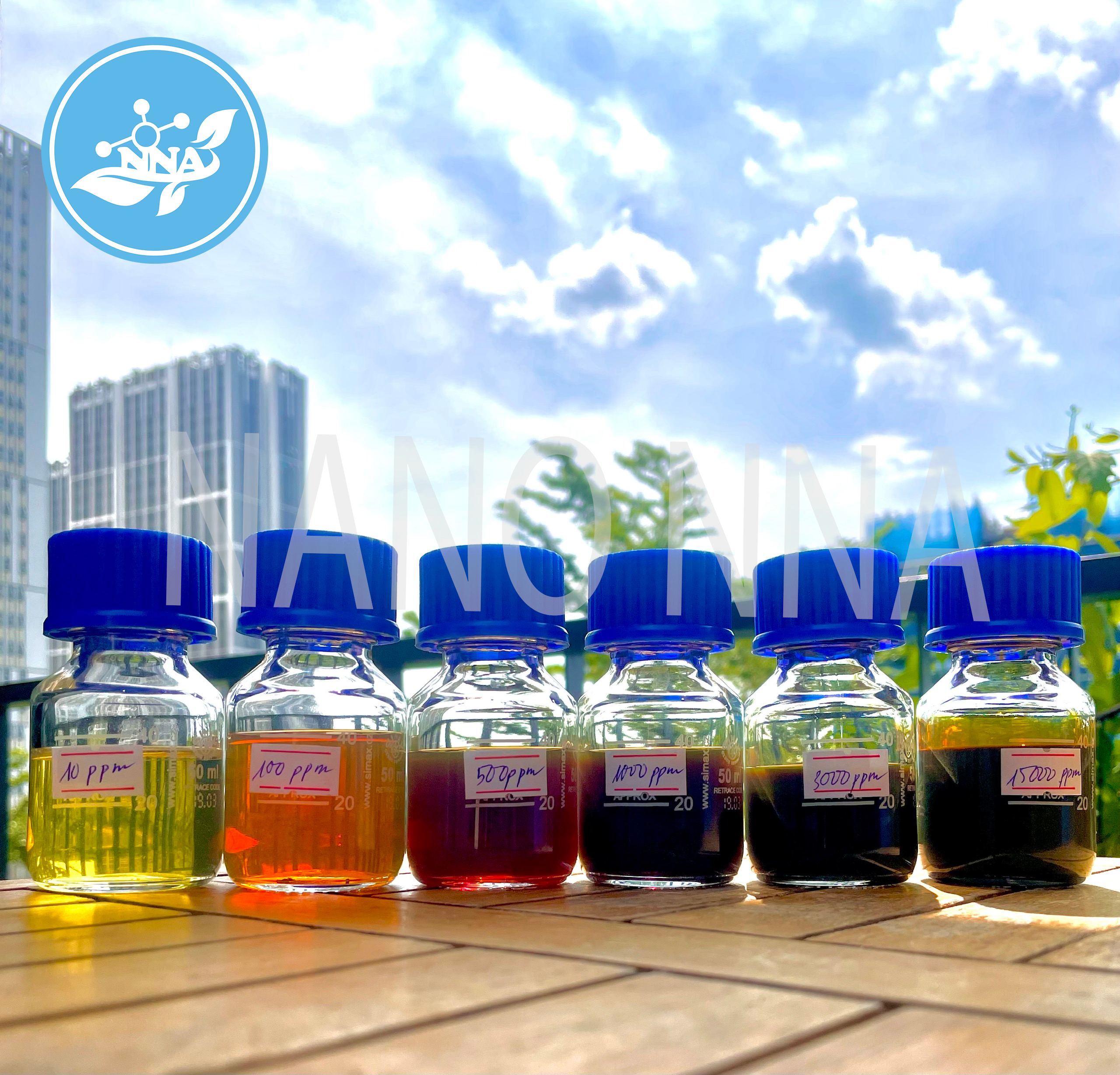
Nano NNA Vietnam is one of the pioneers in the nanotechnology industry, with high concentrations of silver nanoparticles up to 15000ppm. Nano NNA specializes in supplying nano-silver materials to cosmetic, veterinary, aquatic, agricultural, livestock production units, antibacterial fabrics, antibacterial paints, etc. at concentrations of silver nanoparticles 500 ppm, 1000 ppm, 3000 ppm, 5000 ppm and 15000 ppm.
What is Silver Nanoparticles?
Silver nanoparticles, is silver particles with sizes from 1 to 100 nanometers. The reason why silver nano is created by scientists found that silver has natural bactericidal ability and if the contact area of silver is larger, the ability to kill bacteria is higher.
Usually, silver nanoparticles are prepared by a chemical method using pure silver salts as the base. Through the reaction processes will produce Ago metallic silver, because at the nanoscale metal molecules are unstable and tend to stick together, causing silver to accumulate (reducing the ability to kill bacteria), so when producing protective agents will be added to the compartment they stick together.
Many studies around the world have shown the ability of silver nanoparticles to kill bacteria and viruses on more than 650 different strains of bacteria and viruses.
Application of silver nanoparticles material
- Pharmaceutical products (mouthwash, nasal wash, throat spray, body deodorant spray, gynecological wash… from silver nanomaterials)
- Cosmetic chemistry (Cream, facial cleanser, fabric softener… containing silver nanoparticles)
- Livestock ( Silver nanoparticles replaces antibiotics in livestock disease prevention)
- Aquaculture (Taking and feeding silver nanoparticles to replace antibiotics to help prevent aquatic diseases, especially shrimp, fish, snails, frogs, eels, etc.)
- Agriculture (Production of preparations to prevent diseases on plants)
- Latex (Antibacterial Latex)
- Antibacterial Activated Charcoal
- Environment treatment
- Reaction catalyst
- Antibacterial silver nano paint
- Antibacterial silver nano cloth
Three main mechanisms, silver nanoparticles can kill broad-spectrum bacteria
- Because the size of silver nanoparticles is much smaller than that of bacteria, in the environment when silver particles meet bacteria, they will penetrate (like a needle in a bubble) causing abdominal rupture and death.
- The environment around the bacteria is acidic, metal silver will react to produce silver ions (Ag+). This ion has the ability to bind with negatively charged functional groups on the bacterial cell membrane such as -SH, -COOH… causing structural changes leading to death.
- Bacteria will “open their mouth” to absorb nutrients from the outside environment, small silver nanoparticles will get into the bacteria, the acidic environment inside the bacteria will convert silver nano into silver ions. as above) causing metabolic and cellular respiratory disorders leading to death.
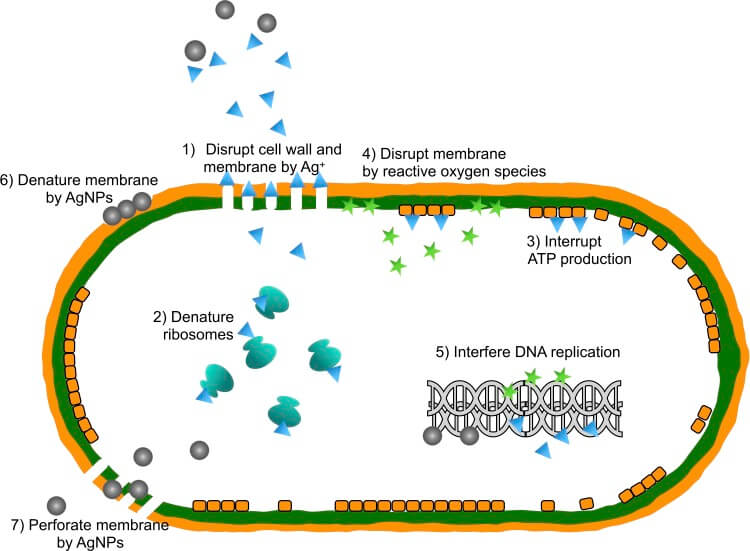
Illustrated image of silver nano-bactericidal mechanism:
Antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs).
Note:
1) Disruption of cell walls and cytoplasmic membranes: silver ions (Ag +) released by silver nanoparticles adhere to or pass through cell walls and cytoplasmic membranes.
2) Ribosome denaturation: silver ions denature the ribosome and inhibit protein synthesis.
3) Interruption of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production: ATP production is terminated because silver ions disable respiratory enzymes on the cytoplasmic membrane.
4) Membrane disruption by reactive oxygen species: the reactive oxygen species produced by the broken electron transport chain can cause membrane disruption.
5) Inhibits the replication of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): reactive oxygen species and silver bind to deoxyribonucleic acid and prevent its replication and cell multiplication.
6) Membrane denaturation: silver nanoparticles accumulate in the pores of the cell wall and cause membrane denaturation.
7) Membrane perforation: silver nanoparticles move directly through the cytoplasmic membrane, which can release organelles out of the cell.
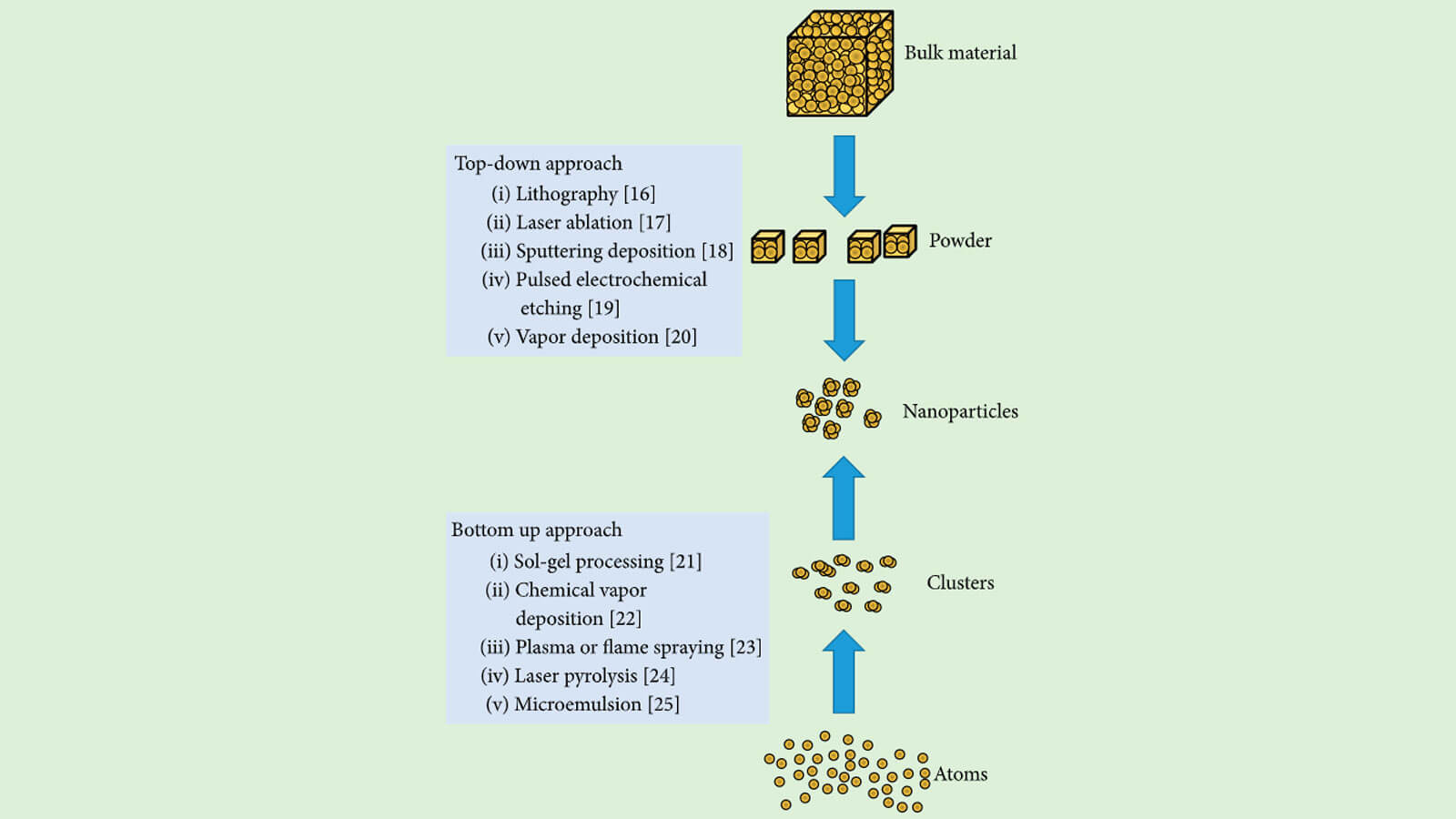
Synthesis of silver nanoparticles
1. Physical method top-down
The principle of this method is to take metal with a large size, and then transform it into nano-sized particles by manufacturing techniques such as: cutting, grinding, grinding… This method can make nanoparticles with sizes from 10 to 100 nm.
However, the top-down method is not really optimal. One of those problems is the uniformity of the grain surface structure. This problem affects the physical and chemical properties of the nanostructured particles due to the large surface area to volume ratio. Despite such a problem, this method can be chosen when making large quantities of silver nanoparticles. One of its applications is in the electronic circuit industry, where nanoscale structures are cut using laser techniques.
Ag+ ions under the action of physical agents. Under the action of commonly used agents such as heat, electromagnetic waves (UV rays, microwaves, lasers, gamma rays, …), ultrasonic waves, Ag + ions are transformed into atomic silver.
Under the action of physical agents, there are many transformations of the solvent or of the substances dispersed or dissolved in the solvent, to produce chemical radicals that reduce Ag+ ions to atomic silver. form nano.
- Methodsbottom-up by chemistry or biology
The principle of this method is to build from atoms, molecules or from chains of molecules. One of the typical bottom-up synthesis methods is the synthesis of nanoparticles from silver nanoparticles systems.
This method uses chemical agents to reduce Ag+ ions to Ag metal atoms, in the presence of electrostatic or surface protective agents, to prevent clumps of metal particles. type of silver, to maintain the silver particles at the nanoscale. The basic principle of the method is expressed by the following equation:
Ag+ + X -> Ag -> nano Ag.
In this method, Ag+ ions, under the action of reducing agent X, will reduce Ag+ ions to Ag metal atoms, then these metal atoms adsorb Ag+ and the Ag+ reduction reaction by X reducing agent, increasing the size of silver metal particles, in the presence of protective agents will form silver nanoparticles with nano size.
Commonly used reducing agents such as: Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4), Ethylene Glycol, Sodium citrate, Ascorbic Acid,…. Surface protectants such as: TSC, PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone), CTAB (Cetrimonium bromide), SDS (Sodium dodecyl sulfate), ….
2. Silver nanoparticle size measurement method
* Method DLS (Dynamic Light Scattering)
Measurement principle: Based on Mie scattering and Fraunhofer diffraction. The device is based on a solid diode laser light source at 650 nm that is passed through a sample cuvette. At an angle of 900 and 1270 to the direction of the light source is a sensor that records the light intensity signal. When the laser beam hits the nanoparticles, the Brownian thermal motion nanoparticles will cause fluctuations in the intensity of the scattered light and are recorded by the sensor. The intensity of the scattered light and the frequency of the oscillation depend on the speed of the nanoparticle’s motion. Smaller particles will move faster under the influence of Brownian motion.
Measurement results: Based on the change in scattered light intensity and recorded frequency, through the Stokes-Einstein equation:

* Methods of TEM (Transmission electron microscopy – Transmission electron microscopy)
- Measuring principle: Similar to a conventional optical microscope, but the light source is no longer visible light but is replaced by an electron emitter. The sample is vacuumed, electrons are accelerated with potential difference from about 80kV – 200kV, through magnetic lenses and scattered by the sample. The image recording and viewing part is a fluorescent screen, when the electron hits the screen, the fluorescent material fluoresces and the image is recorded.
- Measurement results: The measured results are real images of silver nanoparticles, with high accuracy but depending on different areas of the technician’s specimen.
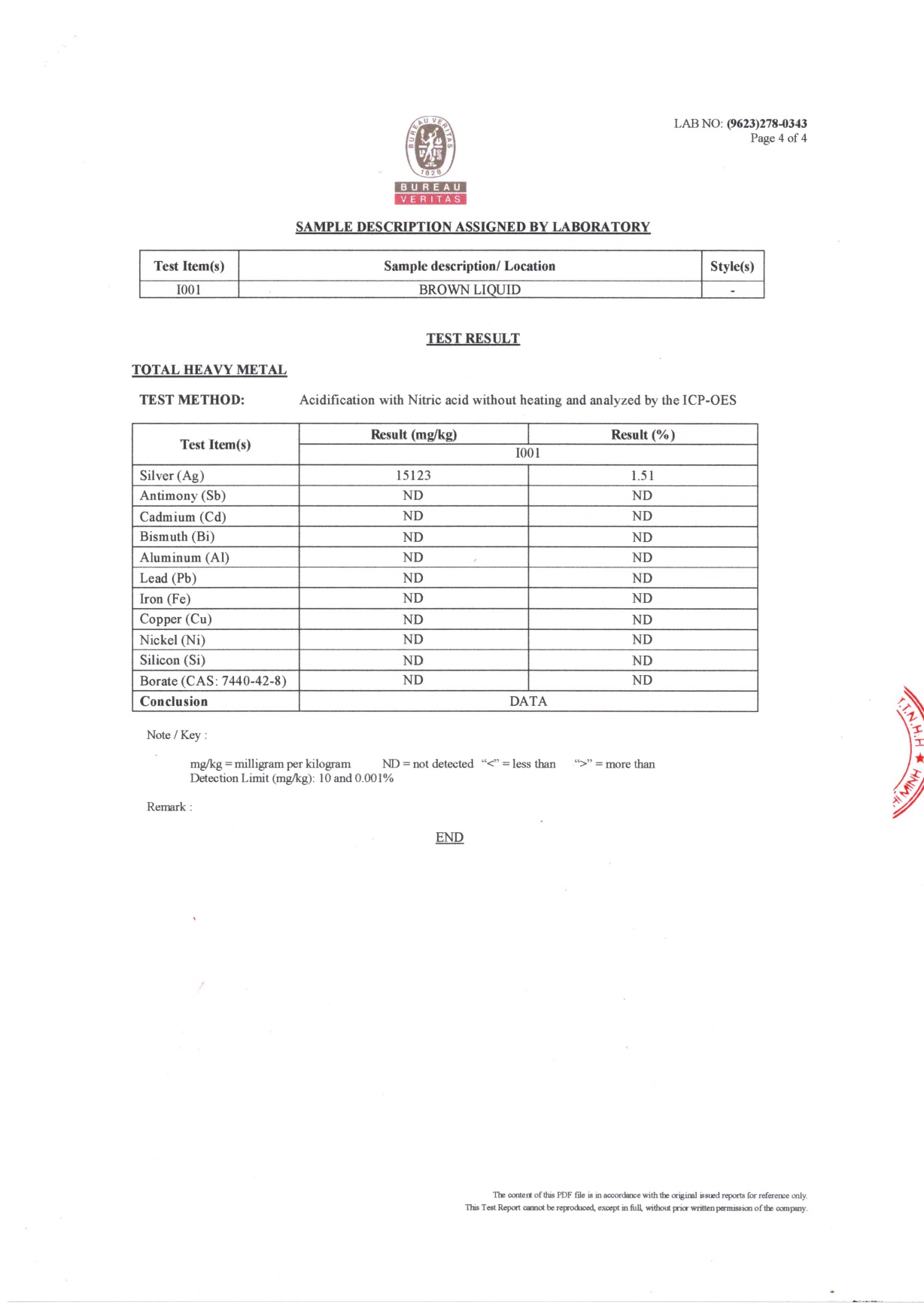
Determination of Ag+ residue in silver nano
According to European pharmacopoeia standards
- Take 0.5g sample to test, add 5ml anhydrous Ethanol and shake for 1 minute (the purpose is to transfer all Ag+ ions from water into ethanol). Then filter to get the solution (in this solution contains Ag+ ions, if any), test the above solution with 2ml concentrated HCl. If no white precipitate is present, the sample is of satisfactory quality.
Conventional rapid identification with 15000 ppm sample.
- Take 0.1g of the sample (total Ag concentration is 15000 ppm), add 15g of distilled water to the sample and shake well until the nanosilver solution is completely dispersed (theoretical total Ag concentration is 100ppm). Take 5ml of the above solution to test with 2ml of 8M NaCl solution. If no white precipitate appears, the sample is qualified.
Theoretical basis:
AgCl <=> Ag+ + Cl–
Equilibrium constant Ksp = [Ag+].[Cl–] = 1.77 x 10-10 (at 250C)
After taking 5ml of solution after diluting it for testing with 2ml of 8M NaCl solution. A solution of about 7ml of solution was obtained, with a total Ag concentration of 71ppm (0.66mM), a Cl– concentration of 2.3M. In order not to appear white precipitate, [Ag+].[Cl–] ≤ 1.77 x 10-10
=> [Ag+] ≤ = = 0.77 x 10-10 M = 0.77 x 10-6 mM
The total Ag content in the sample is 0.66mM .
=> Ag+ content ≤ 1.17 x 10-4 %
Silver nanoparticles material durability
- The durability of silver nanoparticles can be studied by accelerating the aging rate of the product with temperature.
- Theoretical basis:
AgNP → Agmicro
- From the Arrhenius equation, increasing the temperature will increase the value of the reaction rate constant k:
That is, when increasing by 100oC, the reaction rate increases about 3640 times.
- The samples were heated at 130°C for 1 day. Then sensory observation, quantification and evaluation. Evaluation results are similar to storing samples at 30oC for nearly 10 years (1×3640).
- This is true for the case where Ea does not change significantly in the investigated temperature range
* For more information about product and technical advice, please contact hotline: +84909.680.275
???? NANO NNA TECHNOLOGY VIETNAM CO., LTD
???? 1426/39/24 Nguyen Duy Trinh, Long Truong Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City.
???? Contact agent policy: +84909.770.275 or Email: [email protected]
???? Website: nanonna.com










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.